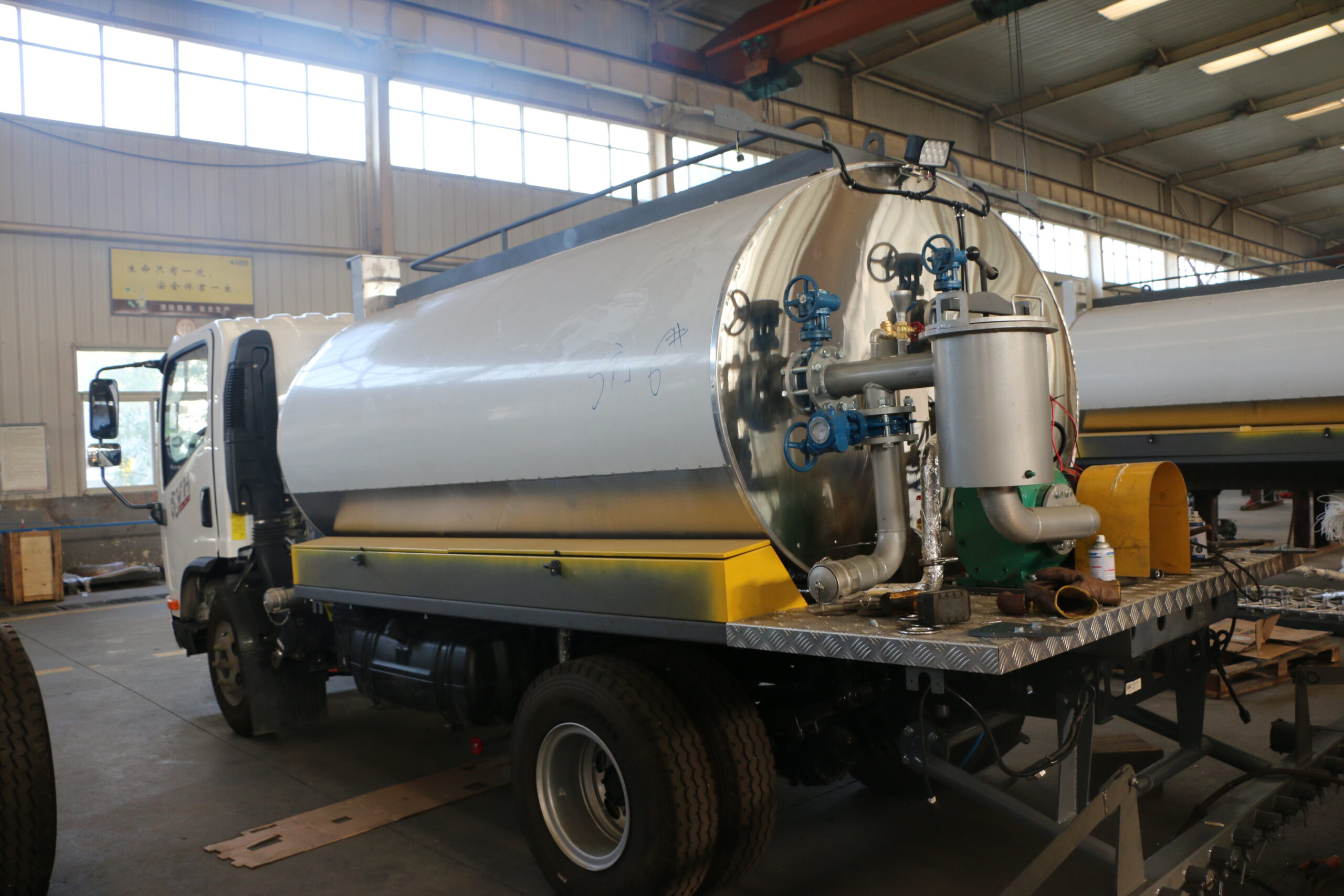
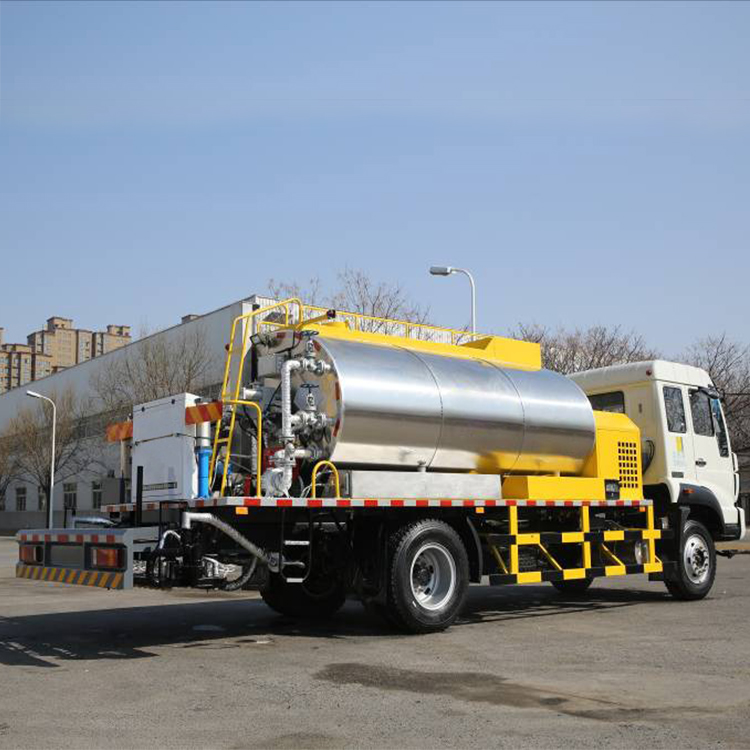
Issues to be noted in the application of slurry seal vehicles
In order to better play the role of slurry seal vehicles, this article explains the matters that should be noted from the aspects of the scope of application, type and material selection, construction technology, common diseases, etc. of slurry seal vehicles.
The slurry seal vehicle is thin in thickness and mainly plays the role of waterproofing, anti-skid, wear-resistant and improving the appearance of the road surface. In the pavement structure system, it can only serve as a surface protection layer and wear layer, but not a load-bearing structure. It is widely used in the construction and maintenance of highways. Practice has proved that the slurry seal can also play an important role by reasonably selecting the thickness and type of the slurry seal and strictly controlling the construction technology and quality.
(1). The scope of application of slurry seal vehicles includes the following aspects:
1. When the pavement damage index of expressways and first-class highways is evaluated as medium and below, or the pavement damage index of second-class and below highways is evaluated as secondary and below, when medium repair and overlay measures should be taken, slurry seal can be selected.
2. When the pavement driving quality index of expressways and first-class highways is evaluated as medium or below, or the pavement driving quality index of second-class and below highways is evaluated as second or below, medium repair and overlay measures should be taken to improve its flatness, and slurry seal can be selected.
3. For sections of expressways and first-class highways with insufficient anti-skid capacity (SFC<40), or sections of second-class and below highways with insufficient anti-skid capacity (SFC<33.5), measures such as adding overlays should be taken to provide anti-skid capacity of the road surface.
4. Anti-skid layer and waterproof protective layer used for third- and fourth-class highways to improve the appearance of the road surface.
In order to better play the role of slurry seal vehicles, this article explains the matters that should be noted from the aspects of the scope of application, type and material selection, construction technology, common diseases, etc. of slurry seal vehicles.
The slurry seal vehicle is thin in thickness and mainly plays the role of waterproofing, anti-skid, wear-resistant and improving the appearance of the road surface. In the pavement structure system, it can only serve as a surface protection layer and wear layer, but not a load-bearing structure. It is widely used in the construction and maintenance of highways. Practice has proved that the slurry seal can also play an important role by reasonably selecting the thickness and type of the slurry seal and strictly controlling the construction technology and quality.
(1). The scope of application of slurry seal vehicles includes the following aspects:
1. When the pavement damage index of expressways and first-class highways is evaluated as medium and below, or the pavement damage index of second-class and below highways is evaluated as secondary and below, when medium repair and overlay measures should be taken, slurry seal can be selected.
2. When the pavement driving quality index of expressways and first-class highways is evaluated as medium or below, or the pavement driving quality index of second-class and below highways is evaluated as second or below, medium repair and overlay measures should be taken to improve its flatness, and slurry seal can be selected.
3. For sections of expressways and first-class highways with insufficient anti-skid capacity (SFC<40), or sections of second-class and below highways with insufficient anti-skid capacity (SFC<33.5), measures such as adding overlays should be taken to provide anti-skid capacity of the road surface.
4. Anti-skid layer and waterproof protective layer used for third- and fourth-class highways to improve the appearance of the road surface.
(2). Selection of the thickness of the slurry sealer. The thickness of the sealer should be selected according to the road surface conditions, traffic types, traffic volume and highway grade.
1. According to the different road damage index and driving quality index, when the slurry sealer is selected for the surface, the thickness of the surface layer should be between 10 and 50 mm.
2. When the sealer is selected according to the traffic volume and the number of heavy-loaded vehicles, the thickness is generally between 3 and 10 mm.
3. According to the different highway grades and the different pavement surface structures, when the anti-skid layer is selected, the thickness is generally between 5 and 40 mm.
(3). Material requirements for slurry sealers. Asphalt binders should be selected from viscous road petroleum asphalt, emulsified asphalt, modified asphalt and modified emulsified asphalt with good performance. Mineral materials should have a certain particle grading composition. The material should be hard, wear-resistant and clean. The sand equivalent technical indicators of the mineral materials should meet the following requirements: ordinary slow-cracking and slow-setting slurry sealer is greater than 45%, and slow-cracking and fast-setting slurry sealer and modified slurry sealer are greater than 65%. Before applying slurry sealing, the composition design of the mix ratio should be carefully done. During construction, the amount of stone, emulsified asphalt, water, filler and additives should be strictly controlled according to the composition design.
(4). The temperature during the construction and maintenance period of the slurry sealer must be greater than 10℃. The original road defects must be treated before sealing. If there are potholes, gnawed edges, cracks, vertical deformations or wide cracks on the original road surface, they should be repaired. For large bumps and deep ruts (such as rut ??depth exceeding 10mm), milling and filling should be carried out. If the base material is found to have poor water stability and other defects, the base should be thoroughly treated first. The original road surface should be cleaned before sealing. Weeds, loose materials, soil and any other obstructive materials on the road surface should be removed. When the porosity of the original road is large or the permeability is high, water cleaning should be avoided, and high-pressure blowing can be used. Cleaning can avoid partial shedding of the sealing road surface.
(5). In order to avoid uneven joints, when sealing, pre-wetting the first paved section with water will help connect the two slurry mixtures. For loose joints and missed paving parts, slurry should be used to fill them in time to make the longitudinal joints smooth. For transverse joints, the best thing is to move forward slowly at a low speed when the paving box is covered with slurry on the entire width at the starting point, so as to reduce the phenomenon of excessive thickness and arching caused by excessive accumulation of materials in the box, and manually level the starting point. After the previous car is sealed, when sealing the next car, it is necessary to go back 3 to 5 meters from the end point of the previous car to start paving the next car; the driver should make the running line of the machine consistent with that of the previous car. When the last car is constructed on this section of road, the end point should be manually leveled and a straight line should be made.
(6). Slurry seal cannot be performed on oily pavement. In order to avoid oily seal, it is necessary to select a suitable oil-to-stone ratio and appropriate water consumption. If the amount of emulsified asphalt is too large, the seal surface will be oily. At this time, the amount of emulsified asphalt should be reduced in time to make the oil-to-stone ratio reach the specified ratio. If the amount of water is large, the stability of the slurry will be reduced, the material will sink, and the asphalt will float, resulting in reduced adhesion with the pavement, and the asphalt content on the seal surface will be too high to cause oily. The amount of water added should be strictly controlled during construction. Generally, when the slump is 2 to 3 cm, its moisture content is appropriate.
(7). The seal pavement is prone to longitudinal scratches. Most of them are due to the mixing of oversized stones in the mineral material, so the mineral material used for construction must be sieved to remove the oversized stones. If large-sized stones are found to be mixed in during construction, they should be removed in time when the scratches are just produced, and the scratches should be repaired.
Practice has proved that slurry seal vehicles have the advantages of low maintenance cost and good maintenance effect. As long as we correctly select the appropriate seal type and thickness in the design, select qualified raw materials in the construction, equip excellent construction machinery and skilled workers, and implement a strict quality inspection system, we can avoid and prevent common diseases of slurry seals and make the slurry seals play a long-term role. The purpose of saving costs and improving road conditions is achieved. This is also an important reason why slurry seal vehicles are valued and promoted.