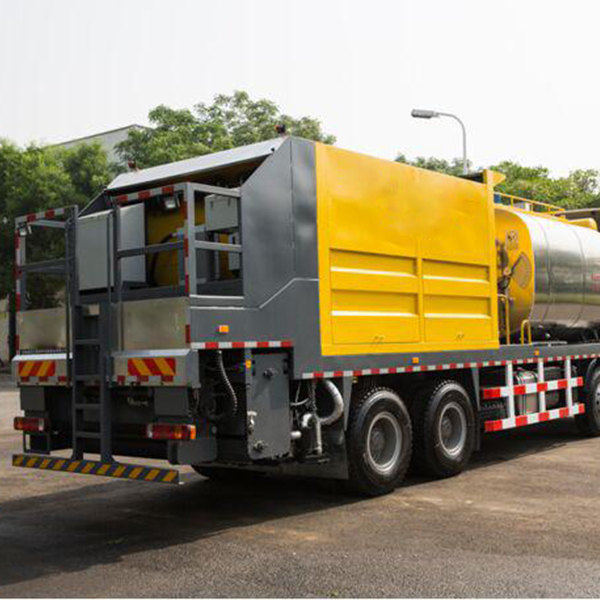
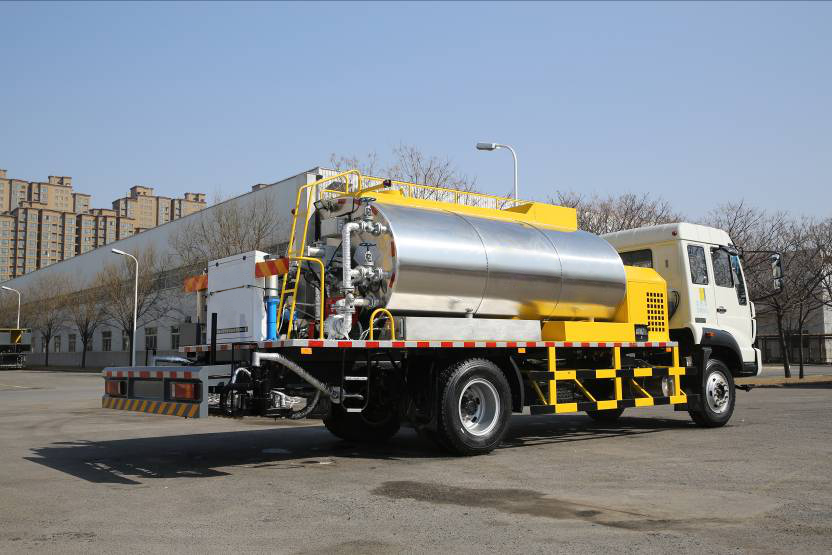
Reasonably control the temperature and viscosity of bitumen decanter machinery and equipment
The viscosity of the drum bitumen decanter equipment decreases as the temperature increases during the production process. Its output viscosity is about twice as high as every 12°C increase. During production, the base bitumen decanter equipment must first be heated to a liquid state and then emulsified. In order to better integrate the emulsification ability of colloid milling, the viscosity of base bitumen decanter is generally controlled to be about 200 cst. The lower the temperature, the higher the viscosity, which increases the pressure on the bitumen decanter pump and colloid milling, making emulsification impossible: However, on the other hand, in order to prevent the bitumen decanter equipment from weaning when the moisture of the finished product evaporates, it is impossible to heat the base asphalt barrel removal temperature too high, and generally use a colloid grinding inlet and outlet system. The finished product temperature should be below 85°C.
The viscosity of the drum bitumen decanter equipment decreases as the temperature increases during the production process. Its output viscosity is about twice as high as every 12°C increase. During production, the base bitumen decanter equipment must first be heated to a liquid state and then emulsified. In order to better integrate the emulsification ability of colloid milling, the viscosity of base bitumen decanter is generally controlled to be about 200 cst. The lower the temperature, the higher the viscosity, which increases the pressure on the bitumen decanter pump and colloid milling, making emulsification impossible: However, on the other hand, in order to prevent the bitumen decanter equipment from weaning when the moisture of the finished product evaporates, it is impossible to heat the base asphalt barrel removal temperature too high, and generally use a colloid grinding inlet and outlet system. The finished product temperature should be below 85°C.
One of the important ways to control the temperature and viscosity of bitumen decanter equipment during production is based on this. We must carry out scientific and standardized operations according to the instructions, so as to fully display its characteristic analysis.