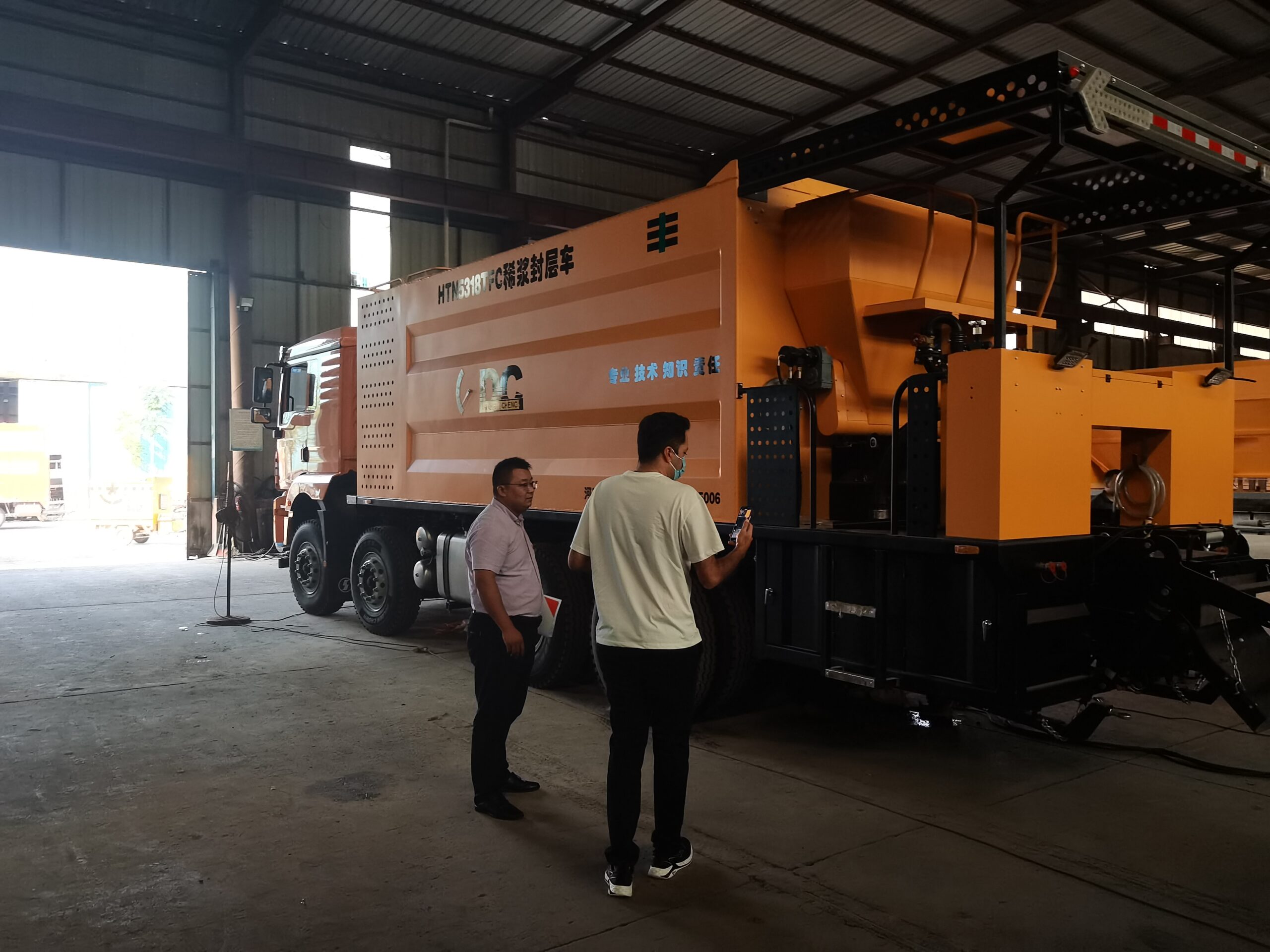
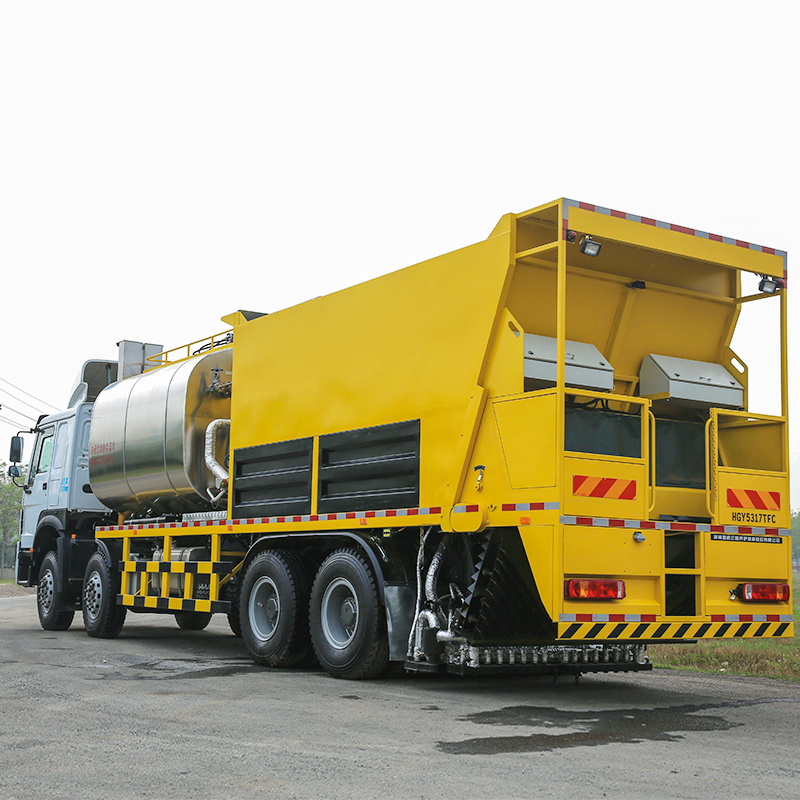
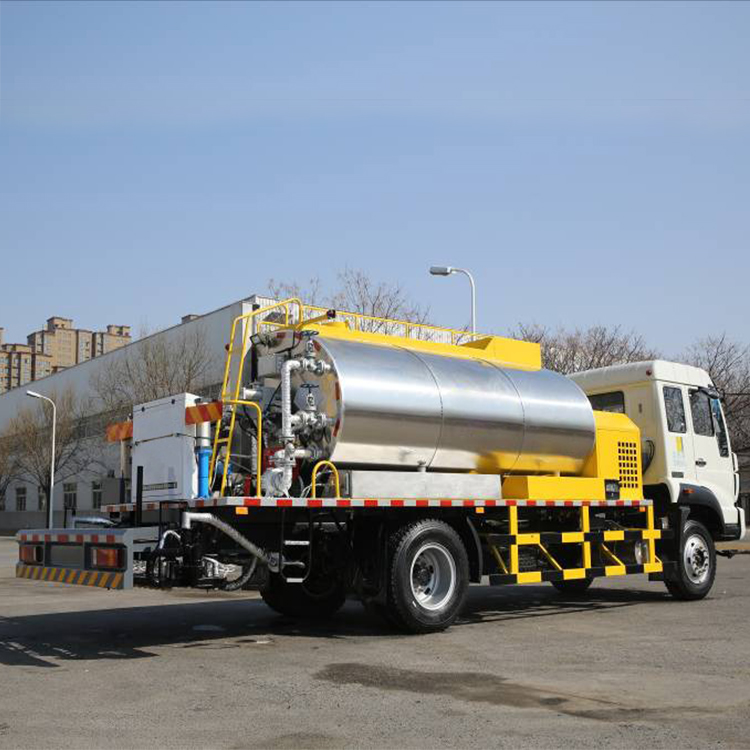
What are the main road uses of modified asphalt equipment?
Contemporary roads and pavements have undergone many changes: traffic volume and driving frequency have increased significantly, the axle load of logistics trucks has continued to increase, one-way driving in separate lanes has been widely implemented, and regulations have further improved the anti-flow resistance of the ground, that is, the work of modified asphalt equipment under high temperatures ability;
Contemporary roads and pavements have undergone many changes: traffic volume and driving frequency have increased significantly, the axle load of logistics trucks has continued to increase, one-way driving in separate lanes has been widely implemented, and regulations have further improved the anti-flow resistance of the ground, that is, the work of modified asphalt equipment under high temperatures ability;
Improve softness and toughness, that is, the ability to resist cracking at low temperatures; improve wear resistance and extend service life. Modern buildings widely use long-span prestressed steel roofs, requiring exterior wall waterproofing materials to be integrated into large offsets. They can also withstand stringent high and low temperature climate conditions, have better performance, are self-adhesive, facilitate construction, and reduce maintenance labor. .